これまでVirtualPC上にCentOSを入れて運用していたのですが、VMwareの方が軽いという話を聞いて乗り換えてみました。(まあ、実はほとんどの場合SSHで接続してCUIで使うのであんまり軽さは関係ないのですが、VMwareの勉強も兼ねまして)
さて、とはいえ環境はなるべくならばそのまま移行したいので、VirtualPCの仮想マシンをそのままVMwareに変換してみました。
ネット上にも参考資料がちらほらありましたが、詳細な手順がなかなか見つからなかったので、ここで詳しい手順をまとめておきます。
仮想マシンのディスクを変換する
VirtualPCでは、仮想マシンのディスクは「.vhd」という拡張子のファイルです。
まずは、これをVMwareのディスクである「.vmdk」形式に変換する必要があります。
この作業のためには「NHC」と呼ばれるソフトを使います。
NHCの使い方
- NHCのサイトへ行きます。
- 「NHC Ver.0 alpha40A 2011/05/14 32bit版」をダウンロードします。
- ダウンロードしたファイルを解凍し、フォルダ内の「NHC.EXE」を起動します。
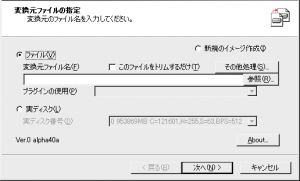
- 「変換元ファイルの指定」で「ファイル」にチェックを入れます。
- 「参照」ボタンをクリックし「.vhd」ファイルを選択します。
- 「変換先の形式の選択」で「組み込み」にチェックを入れ、リストボタンから「VWwareVMDK」を選択します。
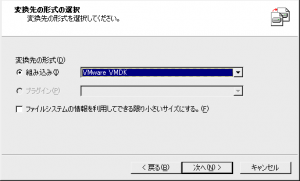
- 「VMware VMDK形式変の変換」に関してはとくに変更せずに「次へ」進みます。
- 「変換先ファイル名」に「.vmdk」をつけたファイル名を入力します。
- 「次へ」をクリックすると変換が始まります。
VirtualPCの設定ファイルをVMware用に変換する
上記でディスクそのものの変換は完了しましたが、個別の設定に関してはさらにVirtualPCの設定ファイル「.vmc」をVMware用の「.vmx」に変換する必要があります。
これにはVMwareの公式サイトから「VMware vCenter Converter Standalone」というソフトをダウンロードして使います。
VMware製品をはじめて利用する場合はユーザー登録が必要ですので、その手順もあわせて説明します。
VMware vCenter Converter Standaloneのダウンロード
- 「VMware vCenter Converter Standalone」のページへ行きます。
- (VMware製品をはじめて利用する場合は)ユーザー登録を行います。
- 登録後届いたメールからユーザーをアクティベートします。
- 同じくもう一通届いているメールから、ソフトのダウンロードページへ移動します。
- ダウンロードしたファイルをダブルクリックで起動してインストールします。
VMware vCenter Converter Standaloneの利用
- プログラム一覧から「VMware vCenter Converter Standalone」を起動します。
- 「マシンの変換」をクリックします。
- 「ソースのタイプを選択」で「バックアップイメージまたはサードパーティ仮想マシン」を選択します。
- 「参照」ボタンから「.vmc」ファイルを選択します。
- 「ターゲットのタイプを選択」で「VWwareWorkStationまたはその他のVMware仮想マシン」を選択します。
- 「VMware製品の選択」で「VMware Player 3.0.x」を選択します。
- 「参照」ボタンから仮想マシンのフォルダを選択します。
- 「オプション」の「ネットワーク」の「接続タイプ」で「NAT」を選択します。
※NATを選ぶとホストOSと共通のIPアドレスが割り振られます。 - 「サマリ」で変換内容を確認したあと「終了」をクリックすると変換が始まります。
VMware Playerの利用
ここまででVirtualPCからの変換作業は完了です。
最後にVMwarePlayerをインストールし、仮想マシンを起動します。
VMware Playerのダウンロード
- VMwarePlayerのページへ行きます。
- 「ダウンロード」へ進むと登録メールアドレスへメールが配信されます。
- 届いたメールからアクティベートを行います。
- 届いたメール内の「VMware Playerのダウンロード」からダウンロードページへ進みます。
- 「VMware Player (32 ビットおよび 64 ビット版 Windows 用)」をダウンロードします。
- ダウンロードしたファイルをダブルクリックで起動してインストールします。
- インストール完了後再起動を求められるので、再起動します。
VMware Playerの利用
- プログラム一覧から「VMware Player」を起動します。
- 「仮想マシンを開く」をクリックします。
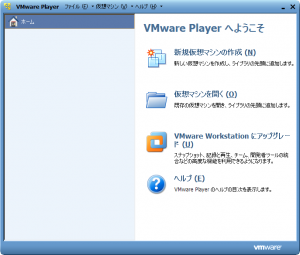
- 作成済みの「.vmx」ファイルを選択すると、左ペインのライブラリ一覧に仮想マシンが追加されます。
- 再生したい仮想マシンを選び「仮想マシンの再生」をクリックすると、仮想マシンが起動します。